RNA medicines: Potential for Germany as a business location
RNA refers to a large group of biomolecules that, following their success in Covid-19 vaccines, are believed to have great potential for prevention and therapy - and thus also for economic success. This opens up opportunities for Germany, as a number of companies and institutes are active in this field here. However, Germany cannot rest on past successes, as researchers in other countries are also active in this field - particularly in the USA and China.
Podcast
Click here to access the vfa-podcast #MicroScope on RNA location Germany directly.
Natural RNA molecules are found in every cell. They fulfill different tasks there. The best known are messenger RNAs (mRNAs). In a sense, they are working copies of genes and are used for the formation of proteins. However, cells always contain RNAs with other functions as well.
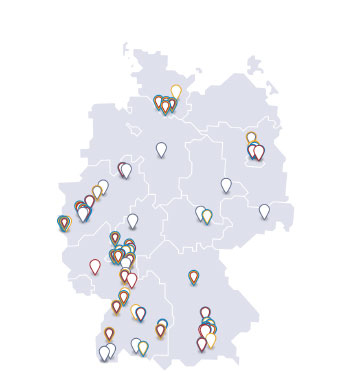
Artificially produced RNA is found, among other things, in vaccines; and a whole range of therapeutics are also currently being developed with it. More and more sites in Germany are active in this field, as the following map shows.
How the location map works
This short explanatory video for the interactive location map shows that the object provides a lot of information and further links. The content can be saved or used in your own web content.
Static version of the map
A static version of the map (of November 2024) can be downloaded as a pdf document in german, in english and as a PNG file in german as well as in english.
As can be seen, there are not only companies in Germany developing mRNA vaccines and other RNA-based medicines, but also suppliers of essential excipients required for their production. The developing companies either carry out the production of the actual medicines themselves or transfer it to contract manufacturers for individual manufacturing steps or the entire production. Research institutes also contribute, especially with the further development of methods for the use of RNA in medicines, usually in cooperation with individual companies. For example, the automation of mRNA production is being optimized at seven institutes of the Fraunhofer-Gesellschaft as part of the lead project RNAuto.
Thus, competence in all aspects of this field of progress is found in Germany; and the distances for cooperations are short. At the same time, the German RNA landscape is closely networked with partners in other countries: via production cooperations, via research alliances, via the procurement of further auxiliary materials and equipment.
However, even though Germany is strong in the RNA field, it is not the only country with expertise and resources. Also very active in this field are the USA and China, but also Belgium, India, South Korea, Switzerland and others. Germany only has a chance of exploiting its current locational advantages if it keeps its eye on the ball now.
vfa-Podcast #MicroScope on RNA location Germany
Download & Streaming
Follow the vfa's MicroScope-Podcast free of charge via these platforms:
Spotify |Apple Podcasts | Soundcloud | Amazon Music | Deezer | vfa Podcasts
Projects for medicines with mRNA
Most of the projects using mRNA are still aimed at developing further Covid 19 vaccines. However, companies in Germany and around the world have long been working on vaccines for other infectious diseases, as the vfa shows on its list of mRNA vaccines in development.
Novel therapeutic drugs with mRNA are being developed to treat cancers (e.g. ovarian cancer) and metabolic disorders that are difficult to treat, such as cystic fibrosis.
Projects for medicines with other types of RNA
If the search is extended to include projects involving any form of RNA-based drug, the entries on the German map become even more dense. Instead of mRNA - which enables cells to produce additional proteins - companies and research institutes use, for example, forms of RNA that block the formation of certain proteins or other substances (so-called antisense RNA or RNAi) by silencing genes (gene silencing). Still others produce aptamers from RNA, molecules that can attach themselves to certain other molecules in a similar way to antibodies to hinder their activity.